Managing Behavioral Challenges in Preschoolers: Effective Parenting Strategies for Ages 2 to 5


Managing Behavioral Challenges in Preschoolers: Effective Parenting Strategies for Ages 2 to 5
 By Inventive Minds Kidz Academy
By Inventive Minds Kidz Academy
 Added Sat, Feb 22 2025
Added Sat, Feb 22 2025
 By Inventive Minds Kidz Academy
By Inventive Minds Kidz Academy
Added Sat, Feb 22 2025
Hey, Thanks For Subscribing!
Please check for a confirmation message and ensure you add us to a safe email list.
If you don't see a message in the next five minutes, check your spam or junk folders and mark our emails safe for next time.
See you soon!
Duplicate Email Found!
Well this is embarrassing... It looks like is already registered.
We have just sent an email to that address with a link to manage the subscription with us. If you don't see a message in the next five minutes, check the spam or junk folders, it's definitely there.
See you soon!

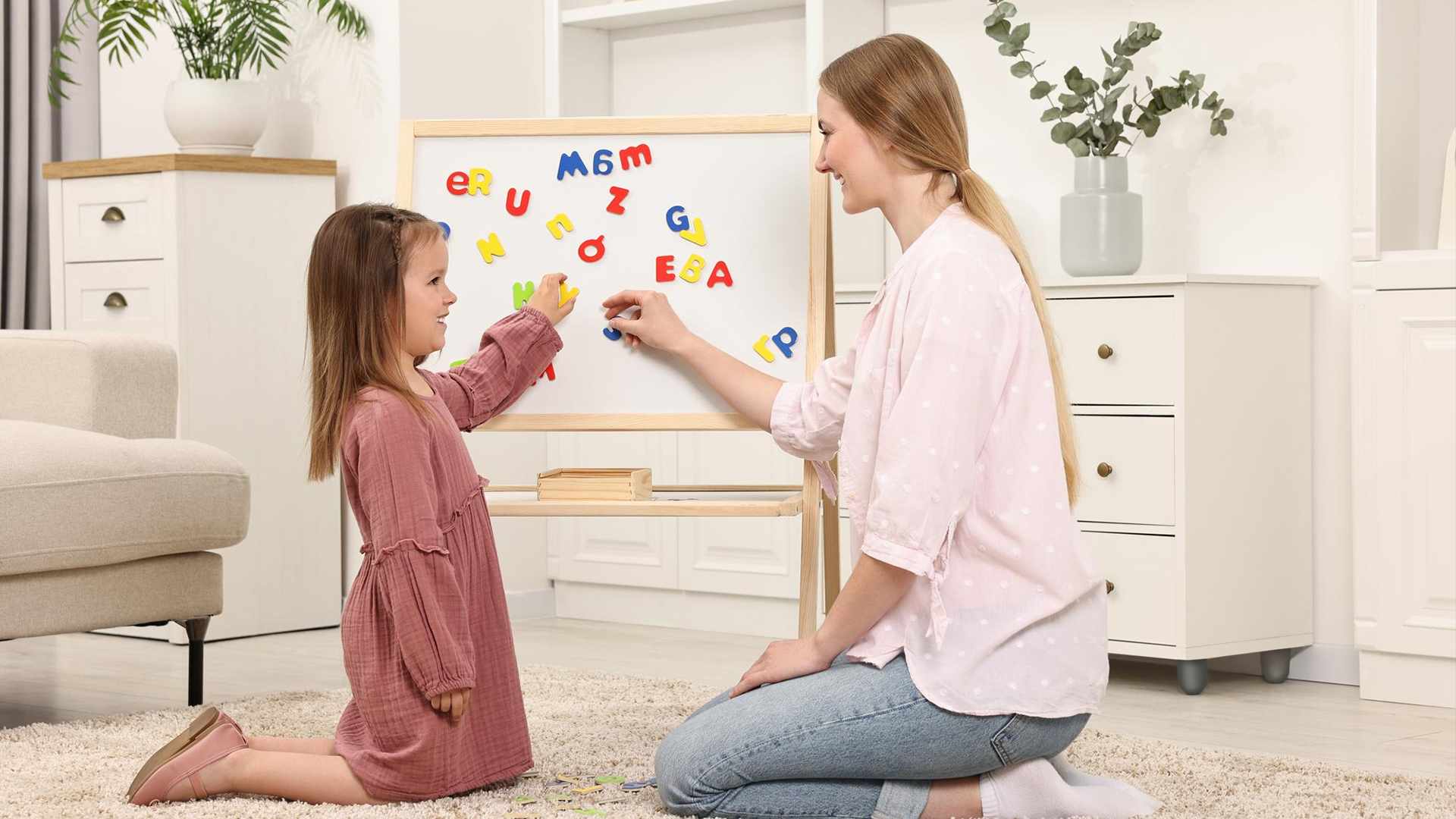
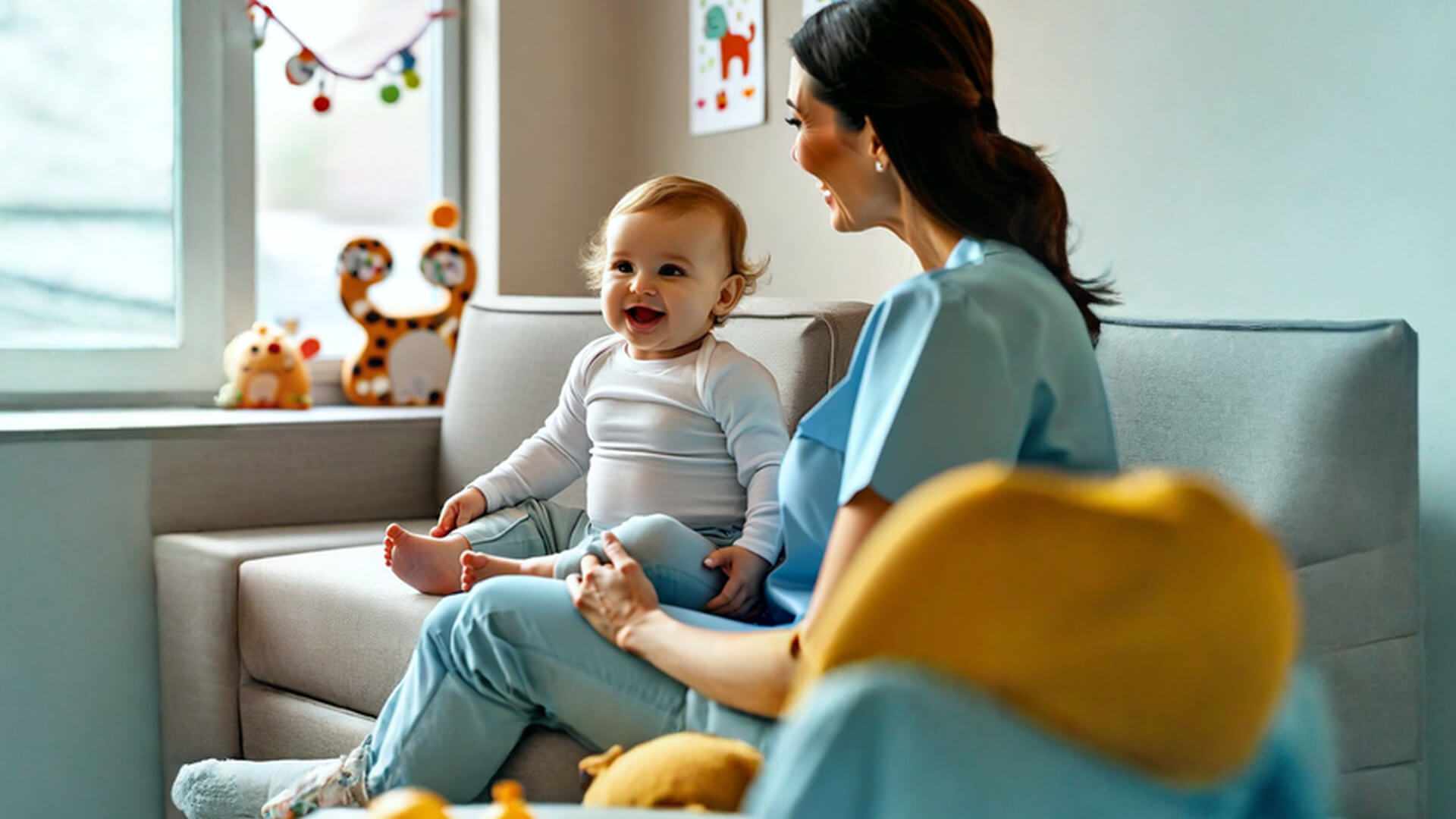
Preschoolers often face behavioral challenges as they navigate emotional and social development. Tantrums, defiance, and emotional outbursts are common during this stage, often triggered by frustration, fatigue, or difficulty expressing needs. Effective management strategies include maintaining predictable routines, teaching emotional regulation techniques like deep breathing, and encouraging children to express feelings with words. Ignoring minor tantrums while providing comfort during distress can also help. By fostering a supportive and structured environment, parents can guide children toward better self-regulation and emotional well-being.
Childhood is a period of rapid development, and behavioral challenges are a natural part of this growth. Many children exhibit difficult behaviors as they navigate their emotions, social interactions, and cognitive development. You as parents play a crucial role in helping children develop self-regulation skills and positive coping mechanisms. This article discusses some of the common behavioral challenges in preschool-aged children, their underlying causes, and strategies for management. According to Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, "behavioral and emotional problems may develop when the temperamental characteristics of children and parents are in conflict. By fostering a supportive and structured environment, caregivers can help children navigate these challenges and build a strong foundation for future emotional and social well-being. “parenting practices significantly influence a child's ability to regulate emotions and develop social competence" as nelson explains.
The "Terrible Twos" and Emotional Dysregulation
The "terrible twos" is a well-recognized developmental phase where toddlers, typically between 18 months and 3 years old, experience frequent tantrums, defiance, and emotional outbursts. According to the Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, "the emergence of language and exposure of children to an expanding social sphere represent critical milestones for children aged 2 to 5 years." During this period, toddlers struggle with emotional regulation due to their developing prefrontal cortex and limited verbal abilities. Tantrums are often triggered by frustration, fatigue, hunger, or difficulty expressing needs.
Effecive Toddler Tantrum Management Strategies
Maintaining predictable routines is one of the most effective toddler tantrum prevention strategies. A consistent daily schedule, including set times for meals, naps, and play, helps children feel secure and reduces the likelihood of emotional outbursts. Predictability minimizes stress and gives children a sense of control over their environment.
Teaching emotional regulation can empower toddlers to manage their feelings. Parents can model and encourage simple emotional regulation techniques, such as deep breathing or using words to express feelings. For example, teaching a toddler to say, "I'm mad" instead of acting out can gradually improve self-regulation skills and reduce the frequency of tantrums.
Ignoring minor tantrums may feel counterintuitive, but it can prevent reinforcing negative behavior. However, if a tantrum stems from genuine distress, offering comfort and reassurance teaches children self-soothing techniques and shows that their emotions are acknowledged. Combining this approach with positive reinforcement, such as verbal praise ("Great job using your words!"), stickers, or a favorite activity, reinforces self-control and encourages calm behavior.
Aggression and Impulsivity in Toddlers
Preschool-aged children may exhibit aggressive behaviors, such as hitting, biting, or pushing, especially in social settings like daycare or playgrounds. Impulsivity is also common due to ongoing brain development. According to Nelson, "aggressive behaviors are a common manifestation of frustration and difficulties in self-regulation during early childhood."
Strategies on How to Stop Toddler Biting and Hitting
Teaching alternative expressions is key to curbing toddler aggression. Encouraging children to verbalize their feelings rather than resorting to physical aggression can reduce conflict. Role-playing or using dolls helps children practice expressing anger appropriately while developing empathy. Providing physical outlets for toddlers can further prevent aggressive behaviors. Engaging in physical activities like running, jumping, or playing with soft balls allows children to release energy and frustration in a healthy way.
Using time-outs wisely creates a calm-down period rather than a punishment. Creating a designated quiet space for children to regulate their emotions helps them reflect on their behavior and regain control. This approach, paired with encouraging cooperative play and teaching turn-taking skills, can significantly improve social interactions. Avoiding harsh discipline is crucial when managing toddler aggression. Harsh punishment can increase frustration and reinforce aggressive tendencies. Instead, redirect behavior and use constructive discussions to teach acceptable ways to express emotions.
Managing Toddler Separation Anxiety
Separation anxiety is a normal developmental stage that typically peaks around 8 to 14 months but can persist into the preschool years. Children may become clingy, cry excessively, or refuse to be left with other caregivers. The Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics explains that "secure attachment allows children to use their parents to reestablish a sense of well-being after a stressful experience."
To ease toddler separation anxiety, practicing short separations can gradually build a child's confidence. Ensuring safe, positive interactions with new caregivers helps children feel secure even when parents are not present. Establishing consistent goodbyes is another essential strategy. Creating a short, predictable goodbye ritual reassures toddlers without increasing anxiety. Avoid sneaking away, as it can create insecurity and mistrust. Instead, say a loving but firm goodbye, emphasizing that you will return soon.
Toddler Sleep Training Tips for Better Rest
Many preschoolers struggle with bedtime resistance, night awakenings, or nightmares. Sleep disturbances can be linked to overstimulation, inconsistent sleep schedules, or anxiety. According to Nelson, "sleep patterns change significantly during early childhood, and disruptions may be associated with developmental milestones and emotional stressors."
Establishing a calming bedtime routine can significantly improve toddler sleep habits. A predictable routine—such as reading a book, dimming the lights, and engaging in quiet activities—signals that it’s time to sleep. Avoiding screen time before bed is equally important, as blue light from screens interferes with melatonin production, making it harder for children to fall asleep.
Providing comfort objects, like a soft nightlight or special stuffed toy, can further reduce bedtime resistance. Positive reinforcement, such as sticker charts or small rewards, motivates children to follow bedtime routines and adopt healthy sleep habits.
Managing Oppositional Behavior and Power Struggles
As children gain independence, they often test limits and defy authority. Persistent oppositional behavior, characterized by frequent arguing, refusal to follow instructions, and deliberate defiance, can be challenging. Nelson states, "children who struggle with adaptability and have a more difficult temperament are more prone to oppositional behaviors."
To manage oppositional behavior effectively, offering limited choices empowers children while maintaining parental expectations. For example, asking, "Do you want to wear the red or blue shirt?" gives toddlers a sense of control while keeping the parent in charge. Setting clear, consistent rules helps toddlers understand boundaries, especially when explained in age-appropriate language. Implementing natural consequences, like feeling cold after refusing to wear a coat, teaches responsibility without confrontation.
Modeling appropriate behavior encourages toddlers to adopt similar habits. Children learn by observing adults, so demonstrating calm and respectful interactions reinforces positive behavior. Avoiding power struggles is equally important, as engaging in conflict often increases defiance. Instead, redirect attention and reinforce positive behaviors to encourage cooperation.
Conclusion
By using these evidence-based parenting tips for toddler behavior, caregivers can create a nurturing environment that promotes emotional well-being and helps children develop essential self-regulation skills. With patience, consistency, and positive reinforcement, parents can navigate the challenges of early childhood while fostering healthy emotional growth. Whether managing tantrums, teaching emotional regulation, or promoting better sleep habits, these strategies ensure toddlers thrive both socially and emotionally.
References
Nelson textbook of pediatrics 22nd edition
https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/138/6/e20163023/52605/Addressing-Early-Childhood-Emotional-and?autologincheck=redirected
SEO Google Phrases:
how to manage toddler tantrums, effective parenting strategies for preschoolers, common behavioral challenges in early childhood, how to handle the terrible twos, emotional regulation tips for toddlers, preschool behavior management techniques, why toddlers throw tantrums, best ways to calm an upset child, how to teach kids self-regulation, parenting tips for children aged 2 to 5, understanding toddler emotions, how to create a structured routine for kids, child development milestones ages 2 to 5, how to discipline toddlers positively, helping children express emotions
Broad Keywords:
toddler behavior, preschool challenges, child development, emotional regulation, parenting tips, tantrum management, kids mental health, early childhood, preschool routines, child psychology, parenting strategies, social skills for kids, child tantrum solutions, toddler coping skills, self-regulation in children
Trending Phrases:
how to manage emotional outbursts in toddlers, effective strategies for the terrible twos, parenting tips for preschool behavioral challenges, teaching emotional regulation to young children, why routines reduce tantrums in kids
Preschoolers often face behavioral challenges as they navigate emotional and social development. Tantrums, defiance, and emotional outbursts are common during this stage, often triggered by frustration, fatigue, or difficulty expressing needs. Effective management strategies include maintaining predictable routines, teaching emotional regulation techniques like deep breathing, and encouraging children to express feelings with words. Ignoring minor tantrums while providing comfort during distress can also help. By fostering a supportive and structured environment, parents can guide children toward better self-regulation and emotional well-being.
Childhood is a period of rapid development, and behavioral challenges are a natural part of this growth. Many children exhibit difficult behaviors as they navigate their emotions, social interactions, and cognitive development. You as parents play a crucial role in helping children develop self-regulation skills and positive coping mechanisms. This article discusses some of the common behavioral challenges in preschool-aged children, their underlying causes, and strategies for management. According to Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, "behavioral and emotional problems may develop when the temperamental characteristics of children and parents are in conflict. By fostering a supportive and structured environment, caregivers can help children navigate these challenges and build a strong foundation for future emotional and social well-being. “parenting practices significantly influence a child's ability to regulate emotions and develop social competence" as nelson explains.
The "Terrible Twos" and Emotional Dysregulation
The "terrible twos" is a well-recognized developmental phase where toddlers, typically between 18 months and 3 years old, experience frequent tantrums, defiance, and emotional outbursts. According to the Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, "the emergence of language and exposure of children to an expanding social sphere represent critical milestones for children aged 2 to 5 years." During this period, toddlers struggle with emotional regulation due to their developing prefrontal cortex and limited verbal abilities. Tantrums are often triggered by frustration, fatigue, hunger, or difficulty expressing needs.
Effecive Toddler Tantrum Management Strategies
Maintaining predictable routines is one of the most effective toddler tantrum prevention strategies. A consistent daily schedule, including set times for meals, naps, and play, helps children feel secure and reduces the likelihood of emotional outbursts. Predictability minimizes stress and gives children a sense of control over their environment.
Teaching emotional regulation can empower toddlers to manage their feelings. Parents can model and encourage simple emotional regulation techniques, such as deep breathing or using words to express feelings. For example, teaching a toddler to say, "I'm mad" instead of acting out can gradually improve self-regulation skills and reduce the frequency of tantrums.
Ignoring minor tantrums may feel counterintuitive, but it can prevent reinforcing negative behavior. However, if a tantrum stems from genuine distress, offering comfort and reassurance teaches children self-soothing techniques and shows that their emotions are acknowledged. Combining this approach with positive reinforcement, such as verbal praise ("Great job using your words!"), stickers, or a favorite activity, reinforces self-control and encourages calm behavior.
Aggression and Impulsivity in Toddlers
Preschool-aged children may exhibit aggressive behaviors, such as hitting, biting, or pushing, especially in social settings like daycare or playgrounds. Impulsivity is also common due to ongoing brain development. According to Nelson, "aggressive behaviors are a common manifestation of frustration and difficulties in self-regulation during early childhood."
Strategies on How to Stop Toddler Biting and Hitting
Teaching alternative expressions is key to curbing toddler aggression. Encouraging children to verbalize their feelings rather than resorting to physical aggression can reduce conflict. Role-playing or using dolls helps children practice expressing anger appropriately while developing empathy. Providing physical outlets for toddlers can further prevent aggressive behaviors. Engaging in physical activities like running, jumping, or playing with soft balls allows children to release energy and frustration in a healthy way.
Using time-outs wisely creates a calm-down period rather than a punishment. Creating a designated quiet space for children to regulate their emotions helps them reflect on their behavior and regain control. This approach, paired with encouraging cooperative play and teaching turn-taking skills, can significantly improve social interactions. Avoiding harsh discipline is crucial when managing toddler aggression. Harsh punishment can increase frustration and reinforce aggressive tendencies. Instead, redirect behavior and use constructive discussions to teach acceptable ways to express emotions.
Managing Toddler Separation Anxiety
Separation anxiety is a normal developmental stage that typically peaks around 8 to 14 months but can persist into the preschool years. Children may become clingy, cry excessively, or refuse to be left with other caregivers. The Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics explains that "secure attachment allows children to use their parents to reestablish a sense of well-being after a stressful experience."
To ease toddler separation anxiety, practicing short separations can gradually build a child's confidence. Ensuring safe, positive interactions with new caregivers helps children feel secure even when parents are not present. Establishing consistent goodbyes is another essential strategy. Creating a short, predictable goodbye ritual reassures toddlers without increasing anxiety. Avoid sneaking away, as it can create insecurity and mistrust. Instead, say a loving but firm goodbye, emphasizing that you will return soon.
Toddler Sleep Training Tips for Better Rest
Many preschoolers struggle with bedtime resistance, night awakenings, or nightmares. Sleep disturbances can be linked to overstimulation, inconsistent sleep schedules, or anxiety. According to Nelson, "sleep patterns change significantly during early childhood, and disruptions may be associated with developmental milestones and emotional stressors."
Establishing a calming bedtime routine can significantly improve toddler sleep habits. A predictable routine—such as reading a book, dimming the lights, and engaging in quiet activities—signals that it’s time to sleep. Avoiding screen time before bed is equally important, as blue light from screens interferes with melatonin production, making it harder for children to fall asleep.
Providing comfort objects, like a soft nightlight or special stuffed toy, can further reduce bedtime resistance. Positive reinforcement, such as sticker charts or small rewards, motivates children to follow bedtime routines and adopt healthy sleep habits.
Managing Oppositional Behavior and Power Struggles
As children gain independence, they often test limits and defy authority. Persistent oppositional behavior, characterized by frequent arguing, refusal to follow instructions, and deliberate defiance, can be challenging. Nelson states, "children who struggle with adaptability and have a more difficult temperament are more prone to oppositional behaviors."
To manage oppositional behavior effectively, offering limited choices empowers children while maintaining parental expectations. For example, asking, "Do you want to wear the red or blue shirt?" gives toddlers a sense of control while keeping the parent in charge. Setting clear, consistent rules helps toddlers understand boundaries, especially when explained in age-appropriate language. Implementing natural consequences, like feeling cold after refusing to wear a coat, teaches responsibility without confrontation.
Modeling appropriate behavior encourages toddlers to adopt similar habits. Children learn by observing adults, so demonstrating calm and respectful interactions reinforces positive behavior. Avoiding power struggles is equally important, as engaging in conflict often increases defiance. Instead, redirect attention and reinforce positive behaviors to encourage cooperation.
Conclusion
By using these evidence-based parenting tips for toddler behavior, caregivers can create a nurturing environment that promotes emotional well-being and helps children develop essential self-regulation skills. With patience, consistency, and positive reinforcement, parents can navigate the challenges of early childhood while fostering healthy emotional growth. Whether managing tantrums, teaching emotional regulation, or promoting better sleep habits, these strategies ensure toddlers thrive both socially and emotionally.
References
Nelson textbook of pediatrics 22nd edition
https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/138/6/e20163023/52605/Addressing-Early-Childhood-Emotional-and?autologincheck=redirected
SEO Google Phrases:
how to manage toddler tantrums, effective parenting strategies for preschoolers, common behavioral challenges in early childhood, how to handle the terrible twos, emotional regulation tips for toddlers, preschool behavior management techniques, why toddlers throw tantrums, best ways to calm an upset child, how to teach kids self-regulation, parenting tips for children aged 2 to 5, understanding toddler emotions, how to create a structured routine for kids, child development milestones ages 2 to 5, how to discipline toddlers positively, helping children express emotions
Broad Keywords:
toddler behavior, preschool challenges, child development, emotional regulation, parenting tips, tantrum management, kids mental health, early childhood, preschool routines, child psychology, parenting strategies, social skills for kids, child tantrum solutions, toddler coping skills, self-regulation in children
Trending Phrases:
how to manage emotional outbursts in toddlers, effective strategies for the terrible twos, parenting tips for preschool behavioral challenges, teaching emotional regulation to young children, why routines reduce tantrums in kids
Most Talked About Posts
You May Also Like
Staff Picks
Now Trending
Our Newsletter
Duplicate Email Found!
Well this is embarrassing... It looks like is already registered.
We have just sent an email to that address with a link to manage the subscription with us. If you don't see a message in the next five minutes, check the spam or junk folders, it's definitely there.
See you soon!
Join Our Newsletter
Hey, Thanks For Subscribing!
Please check for a confirmation message and ensure you add us to a safe email list.
If you don't see a message in the next five minutes, check your spam or junk folders and mark our emails safe for next time.
See you soon!
Duplicate Email Found!
Well this is embarrassing... It looks like is already registered.
We have just sent an email to that address with a link to manage the subscription with us. If you don't see a message in the next five minutes, check the spam or junk folders, it's definitely there.
See you soon!